The heartbreaking reality of pets without parents affects millions of animals worldwide each year. Whether due to abandonment, natural disasters, or tragic circumstances that separate young animals from their mothers, these vulnerable creatures require specialized care, compassion, and understanding to survive and thrive. This comprehensive guide explores the complex world of orphaned pets, providing essential information for potential caregivers, animal welfare organizations, and anyone interested in making a difference in the lives of these defenseless animals.
Understanding the Crisis of Pets Without Parents
The term “pets without parents” encompasses a broad spectrum of situations where young animals find themselves without maternal care. According to the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA), approximately 6.3 million companion animals enter U.S. animal shelters nationwide every year, with a significant portion being orphaned or abandoned young animals requiring immediate intervention.
Common Causes of Pet Abandonment
Natural Disasters and Environmental Factors Natural catastrophes such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires frequently separate pet families, leaving young animals stranded without their mothers. The National Geographic has documented numerous cases where environmental disasters have created waves of orphaned wildlife and domestic animals requiring human intervention.
Human Irresponsibility Unfortunately, human factors contribute significantly to the pet abandonment crisis. Unplanned breeding, financial hardship, housing restrictions, and lack of education about pet responsibility all play roles in creating situations where animals are left without care.
Medical Emergencies Sometimes, mother animals suffer from medical complications during or after birth, making them unable to care for their offspring. In these cases, human intervention becomes crucial for the survival of the young animals.
Wildlife Interference In some instances, well-meaning humans accidentally separate wildlife mothers from their babies by assuming the young animals are abandoned when they’re actually being cared for in ways not immediately visible to humans.
The Critical Early Stages: Newborn to 8 Weeks

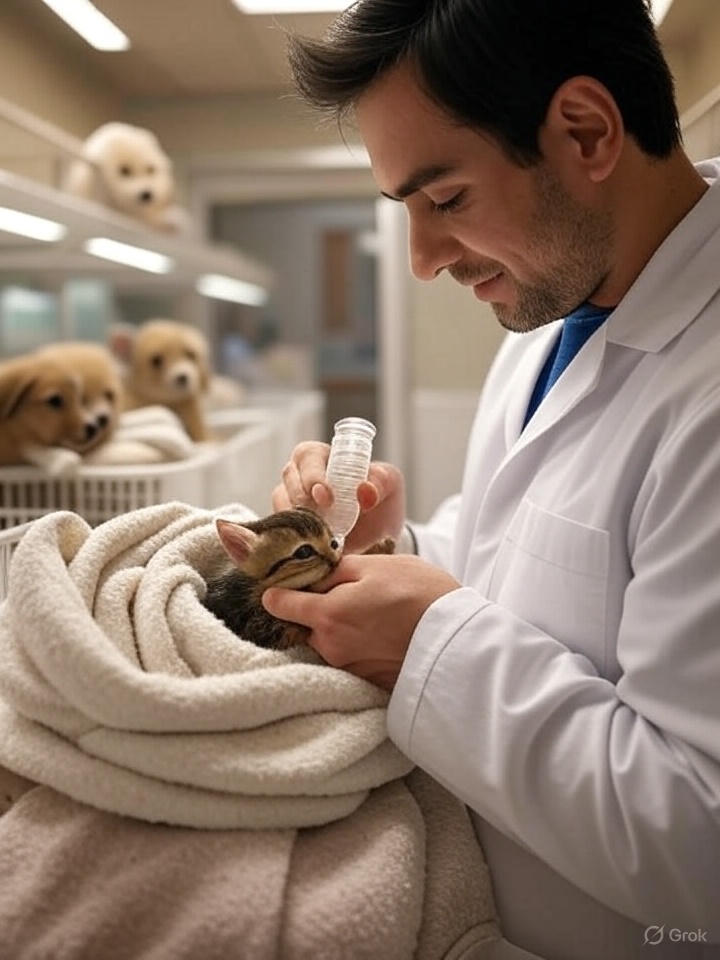
Immediate Care Requirements
The first few hours and days are absolutely critical for pets without parents. Young animals require specific care that mimics what they would receive from their mothers:
Temperature Regulation Newborn animals cannot regulate their body temperature effectively. Creating a warm, stable environment using heating pads, blankets, or specialized incubators is essential for survival. The ideal temperature varies by species but generally ranges from 85-90°F for the first week of life.
Nutrition and Feeding Proper nutrition is perhaps the most crucial aspect of caring for orphaned pets. Species-specific milk replacers must be used, as cow’s milk can cause digestive issues in most young animals. Feeding schedules are typically every 2-3 hours for very young animals, gradually extending as they grow.
Hygiene and Stimulation Mother animals typically stimulate their young to urinate and defecate. Caregivers must replicate this process using warm, damp cloths to gently stimulate the genital and anal areas after each feeding.
Species-Specific Considerations
Different species have varying needs when orphaned. For example, understanding rabbit anatomy and their fragile spine and prey instincts is crucial when caring for orphaned rabbits, as their delicate nature requires specialized handling techniques.
Puppies and Kittens
- Eyes typically open at 10-14 days
- Begin weaning process at 3-4 weeks
- Require socialization with humans and other animals
- Need multiple vaccinations starting at 6-8 weeks
Small Mammals (Rabbits, Guinea Pigs, Hamsters)
- Often have shorter gestation periods and faster development
- May require specialized diets rich in specific nutrients
- Need careful temperature control due to their small size
- Benefit from species-appropriate socialization
Birds
- Require hand-feeding with specialized formulas
- Need consistent feeding schedules every 2-4 hours
- Require appropriate nesting materials and temperature control
- May need assistance with feather development and flight training
The Psychological Impact on Pets Without Parents
Behavioral Challenges
Animals separated from their parents often experience psychological trauma that can manifest in various behavioral issues. Research published in Applied Animal Behaviour Science indicates that early separation can lead to:
Attachment Issues Pets without parents may develop either excessive attachment to human caregivers or difficulty forming bonds altogether. This can result in separation anxiety, destructive behavior, or social withdrawal.
Fear and Anxiety Without proper maternal teaching, orphaned animals may not learn appropriate fear responses or may develop excessive anxiety about normal situations. This can impact their ability to adapt to new environments and situations.
Social Skill Deficits Mother animals teach their young crucial social skills, including communication with other animals, appropriate play behavior, and boundaries. Orphaned pets may struggle with these skills throughout their lives.
Building Resilience and Confidence
Successful rehabilitation of pets without parents requires intentional efforts to build their confidence and resilience:
Gradual Exposure Introducing new experiences, sounds, textures, and environments gradually helps orphaned pets develop confidence and adaptability.
Positive Reinforcement Training Early training using positive reinforcement techniques helps build trust between the animal and human caregivers while establishing important behavioral foundations.
Socialization Opportunities When medically appropriate, supervised interactions with other animals can help orphaned pets learn crucial social skills they would typically learn from their mothers and siblings.
Medical Considerations and Health Monitoring
Common Health Issues
Pets without parents face increased health risks due to their compromised start in life:
Immune System Vulnerabilities Without maternal antibodies from nursing, orphaned animals have weakened immune systems and increased susceptibility to infections and diseases.
Nutritional Deficiencies Improper feeding or inadequate nutrition during critical growth periods can lead to developmental issues, bone problems, and organ dysfunction.
Stress-Related Conditions The trauma of separation and the stress of artificial rearing can manifest in various health problems, including digestive issues, skin conditions, and behavioral abnormalities.
Preventive Care Protocols
Establishing comprehensive preventive care is essential for orphaned pets:
Regular Veterinary Monitoring Frequent check-ups allow for early detection and treatment of health issues. The American Veterinary Medical Association recommends more frequent visits for orphaned animals compared to those raised by their mothers.
Vaccination Schedules Orphaned pets may require modified vaccination schedules to account for their lack of maternal antibodies and increased vulnerability to diseases.
Nutritional Monitoring Regular weight checks and body condition assessments ensure proper growth and development. Nutritional adjustments may be necessary based on individual needs and species requirements.
The Role of Foster Care and Rescue Organizations
Professional Foster Programs
Many animal welfare organizations have developed specialized foster programs for pets without parents:
Training and Support Reputable organizations provide comprehensive training for foster caregivers, covering species-specific care requirements, emergency protocols, and behavioral development.
Medical Support Professional rescue organizations typically provide veterinary care, medications, and emergency support for foster families caring for orphaned animals.
Placement Services These organizations also handle the adoption process, ensuring that successfully raised orphaned pets find appropriate permanent homes.
The Economics of Pet Rescue
According to Forbes, the pet industry is worth over $260 billion globally, yet funding for orphaned animal care remains limited. The cost of properly caring for pets without parents can be substantial, including:
- Specialized milk replacers and feeding supplies
- Veterinary care and medications
- Temperature control equipment
- Time investment for round-the-clock care
- Behavioral rehabilitation services
Technology and Innovation in Pet Care
Digital Tools for Caregivers
Modern technology has revolutionized the care of orphaned pets. Digital platforms and tools now assist caregivers in:
Monitoring and Tracking • Weight tracking applications • Feeding schedule reminders • Growth milestone documentation • Medical record management • Comprehensive pet care resources
Educational Resources Online platforms provide access to species-specific care guides, video tutorials, and expert advice for caring for pets without parents.
Community Support Digital communities connect caregivers with experienced foster families, veterinarians, and animal behavior specialists for guidance and support.
Innovative Care Solutions
Technological advances have led to improved care options:
Automated Feeding Systems Specialized feeding devices can provide consistent nutrition on schedule, particularly helpful for caregivers managing multiple orphaned animals.
Environmental Control Systems Advanced incubators and heating systems provide precise temperature and humidity control for optimal growth environments.
Telemedicine Services Remote veterinary consultations allow for immediate professional guidance when caring for orphaned pets, particularly valuable in emergency situations.
Success Stories and Rehabilitation Outcomes
Long-term Studies and Research
Research from Cornell University’s College of Veterinary Medicine has shown that with proper care, many orphaned pets can develop into healthy, well-adjusted adults. Success factors include:
Early Intervention The sooner appropriate care begins, the better the outcomes for orphaned animals. Immediate medical attention and proper nutrition in the first 24-48 hours significantly improve survival rates.
Consistent Caregiving Animals that receive consistent care from dedicated caregivers show better behavioral and health outcomes compared to those experiencing multiple caregiver changes.
Species-Appropriate Rehabilitation Programs that account for species-specific needs and natural behaviors produce more successful outcomes than generic care approaches.
Measuring Success
Success in caring for pets without parents is measured through various metrics:
Survival Rates Professional foster programs report survival rates of 70-85% for orphaned pets when proper care protocols are followed.
Adoption Success Successfully rehabilitated orphaned pets have adoption rates comparable to animals raised by their mothers when proper socialization has occurred.
Long-term Health Outcomes Follow-up studies indicate that properly cared for orphaned pets can live normal lifespans with appropriate ongoing care.
Prevention and Education Initiatives
Community Outreach Programs
Preventing the pet abandonment crisis requires comprehensive community education:
Spay and Neuter Campaigns The Humane Society of the United States promotes spay and neuter programs as the most effective method for reducing pet overpopulation and subsequent abandonment.
Responsible Pet Ownership Education Educational programs teach potential pet owners about the long-term commitment and responsibility involved in pet ownership, helping prevent impulse decisions that lead to abandonment.
Emergency Preparedness Community programs help pet owners prepare for natural disasters and emergencies, reducing the likelihood of pet separation during crises.
Legislative Efforts
Many jurisdictions have implemented laws aimed at reducing pet abandonment:
Anti-Abandonment Legislation Laws that penalize pet abandonment help deter irresponsible behavior while providing legal recourse for animal welfare organizations.
Breeder Regulations Stricter breeding regulations help prevent puppy mills and irresponsible breeding practices that contribute to pet overpopulation.
Support for Rescue Organizations Government funding and tax incentives for animal rescue organizations help support their efforts in caring for pets without parents.
The Future of Orphaned Pet Care
Emerging Trends and Innovations
The field of orphaned pet care continues to evolve with new research and innovations:
Genetic Research Studies into the genetic factors that influence survival and development in orphaned animals may lead to improved care protocols and selection criteria for breeding programs.
Behavioral Science Advances Ongoing research into animal behavior and psychology continues to improve our understanding of how to best support the emotional and behavioral development of pets without parents.
Collaborative Care Models New models that combine professional veterinary care with trained volunteer foster families are showing promising results in improving outcomes while managing costs.
Global Perspectives
The issue of pets without parents is global, with different regions facing unique challenges:
Developing Nations Countries with limited veterinary infrastructure face greater challenges in caring for orphaned pets, leading to international cooperation and aid programs.
Urban vs. Rural Differences Urban areas typically have more resources for orphaned pet care but may face different types of abandonment issues compared to rural regions.
Cultural Considerations Different cultural attitudes toward animals influence how societies approach the care of pets without parents, affecting resource allocation and community support.
Conclusion: Building a Compassionate Future
The challenge of caring for pets without parents requires a multifaceted approach combining immediate care, long-term rehabilitation, prevention efforts, and community support. Success depends on the dedication of foster caregivers, the expertise of veterinary professionals, the support of rescue organizations, and the commitment of communities to address the root causes of pet abandonment.
As our understanding of animal behavior, nutrition, and medical care continues to advance, the outcomes for orphaned pets continue to improve. Technology provides new tools for caregivers, while research offers insights into best practices for rehabilitation and long-term care.
The responsibility for addressing the crisis of pets without parents extends beyond individual caregivers to encompass entire communities, governments, and society as a whole. Through education, legislation, and compassionate action, we can work toward a future where fewer animals experience the trauma of abandonment and those who do receive the care they need to thrive.
Every pet without parents represents both a tragedy and an opportunity – a tragedy of circumstances that separated them from their natural care, but an opportunity for humans to demonstrate compassion, dedication, and the remarkable capacity to heal and nurture vulnerable life. The investment in caring for these animals pays dividends not only in their survival and wellbeing but in the development of more compassionate communities and the advancement of our understanding of animal welfare.
By supporting rescue organizations, volunteering as foster caregivers, promoting responsible pet ownership, and advocating for protective legislation, each person can contribute to addressing the crisis of pets without parents. The goal is not just survival, but creating opportunities for these resilient animals to experience the love, security, and care that every pet deserves.
The future of orphaned pet care looks increasingly promising, with continued advances in veterinary medicine, animal behavior science, and community support systems. As we move forward, the lessons learned from caring for pets without parents continue to inform and improve our approach to animal welfare as a whole, creating a more compassionate world for all animals.




Pingback: 10 Great First Pets - Snapspeak